Forex Trading Explained: A Beginner’s Guide
 Tom Foster
Tom Foster
07/12/2024
193 Views
What is Forex?
Forex (FX), short for foreign exchange, is a global marketplace where currencies are traded. This means you buy one currency and sell another simultaneously, always in pairs, such as EUR/USD or USD/JPY. The forex market is decentralized, operating 24 hours a day across major financial hubs, including London, New York, Tokyo, and Sydney.
It is the largest and most liquid financial market globally, with an estimated daily trading volume of $918.4 billion in 2023. The market’s size and activity level make it attractive to retail and institutional traders alike. Unlike stock markets, forex trading is conducted over-the-counter (OTC), which means trades occur directly between participants rather than on a centralized exchange.
Forex Pairs
Currencies are always traded in pairs, with one currency as the base (e.g., EUR) and the other as the quote (e.g., USD). The quoted price indicates how much of the quote currency is needed to purchase one unit of the base currency. Forex pairs are divided into three categories:
- Major Pairs: These include the most traded pairs globally, such as EUR/USD, GBP/USD, and USD/JPY.
- Minor Pairs: Pairs that do not include the US Dollar, such as EUR/GBP or AUD/JPY.
- Exotic Pairs: Combinations of major currencies with emerging market currencies like USD/TRY or EUR/SEK.
The forex market’s accessibility, high liquidity, and leverage options make it a popular choice among traders. However, it is equally important to understand the risks involved.
Fundamental Analysis: The Role of Global Events
Fundamental analysis in forex trading involves understanding the underlying economic and political factors that influence currency values. A deep understanding of these factors can help traders anticipate market trends and make informed decisions.
Key Components of Fundamental Analysis:
- Economic Indicators:
- GDP Growth: A strong GDP indicates a healthy economy, often strengthening a currency.
- Interest Rates: Higher interest rates generally attract foreign investment, boosting currency demand.
- Inflation: Moderate inflation is often favorable, but hyperinflation can devalue a currency.
- Employment Data: High employment levels signify economic stability, supporting currency strength.
- Geopolitical Events: Political instability, elections, or trade wars can create market volatility. For instance, Brexit significantly impacted the GBP/USD pair.
- Central Bank Policies: Central banks influence currency markets through monetary policy. Announcements like interest rate hikes or quantitative easing by entities such as the Federal Reserve or the European Central Bank often have immediate market repercussions.
Keeping up with financial news, analyzing reports, and understanding the global economy are crucial for effective fundamental analysis.
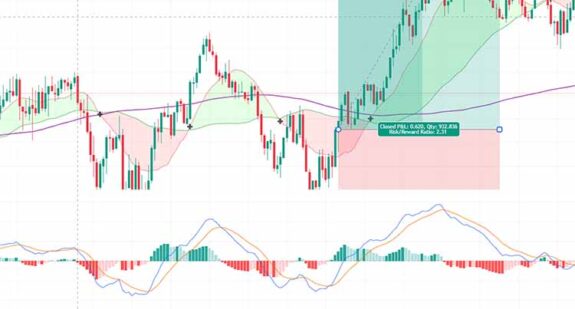
Technical Analysis: Interpreting Market Movements
Technical analysis involves studying past price movements to predict future trends. Unlike fundamental analysis, which focuses on macroeconomic data, technical analysis relies on charts, patterns, and indicators to identify trading opportunities.
Popular Techniques:
- Chart Patterns: Visual representations of price movements that signal market behavior. Examples include:
- Head and Shoulders: Indicates potential trend reversals.
- Triangles: Suggest continuation or breakout patterns.
- Technical Indicators:
- Moving Averages: Help identify trends by smoothing price data over a specified period.
- RSI (Relative Strength Index): Measures the strength of price movements to detect overbought or oversold conditions.
- MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence): Highlights potential buy or sell signals based on momentum.
- Candlestick Patterns: Widely used for short-term trading analysis. Patterns like dojis, hammers, and engulfing candles can reveal market sentiment.
Mastering these tools requires practice, but they are invaluable for building a disciplined trading approach.
Start Trading Today with These Top Brokers:
*Plus500 Risk Warning: 82% of retail CFD accounts lose money
Risk Management: Protecting Your Capital
Risk management is arguably the most critical aspect of forex trading. Effective risk management minimizes potential losses and ensures long-term trading sustainability.
Key Strategies:
- Stop-Loss Orders: Automatically close trades when the price reaches a specified loss limit, protecting your account from excessive losses.
- Take-Profit Orders: Secure gains by exiting trades at predetermined profit levels.
- Position Sizing: Allocate an appropriate portion of your trading capital per trade, typically no more than 1–2% of your total account balance.
- Risk-Reward Ratio: Strive for a favorable risk-reward ratio, such as risking $1 to potentially earn $2 or more.
Understanding your risk tolerance is essential. Over-leveraging or emotional trading can quickly lead to substantial losses.
Trading Strategies: Finding Your Approach
The forex market accommodates various trading styles, each catering to different goals, time commitments, and risk tolerances.
Popular Strategies:
- Day Trading: Involves executing multiple trades within a single day to profit from intraday price movements. Requires constant monitoring and quick decision-making.
- Swing Trading: Focuses on capturing short-to-medium-term trends. Trades typically last several days or weeks, making it less demanding than day trading.
- Position Trading: A long-term approach based on fundamental analysis. Traders hold positions for weeks, months, or even years.
Experimenting with strategies and adapting them to your trading personality can enhance performance.
Trading Psychology: The Human Element
Emotions play a significant role in trading outcomes. Controlling fear, greed, and overconfidence is vital for consistent performance.
Tips for Mastering Trading Psychology:
- Avoid Common Mistakes:
- Overtrading: Excessive trading without a clear plan.
- Revenge Trading: Attempting to recover losses impulsively.
- Develop a Trading Plan: Outline your objectives, preferred strategies, and risk management rules.
- Practice Discipline: Adhering to your plan, even in volatile conditions, fosters long-term success.
Successful traders recognize that patience and emotional resilience are just as important as technical skills.
Conclusion: Educate and Prepare
Forex trading offers exciting opportunities but comes with substantial risks. Aspiring traders must focus on continuous education, practice with demo accounts, and implement sound risk management strategies. Whether leveraging fundamental insights, mastering technical tools, or refining trading psychology, preparation is key to navigating the complexities of the forex market.